Process materials for die-casting: Various materials and processes are crucial decisions before production

Introduction:
In the realm of modern manufacturing, die casting holds a prominent position, offering unparalleled precision and efficiency in crafting intricate metal parts. From automotive components to electronic devices, die casting shapes various industries. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the principles, equipment, materials, techniques, and classifications of die casting, providing readers with a deeper understanding of this versatile manufacturing process.
1. Understanding Die Casting Principles:
At the core of die casting lies the creation of molds, meticulously designed to replicate the intricate details of desired parts. Molten metal, typically aluminum, magnesium, or zinc alloys, is then injected into these molds under high pressure. As the metal cools and solidifies, it conforms to the mold cavity, resulting in precise and complex parts.
2. Exploring Die Casting Equipment:
Die casting relies on a range of equipment, each playing a crucial role in the manufacturing process. Die casting machines, molds, and furnaces are key components involved. These machines come in various sizes and configurations, facilitating the production of parts ranging from small components to large structural pieces.
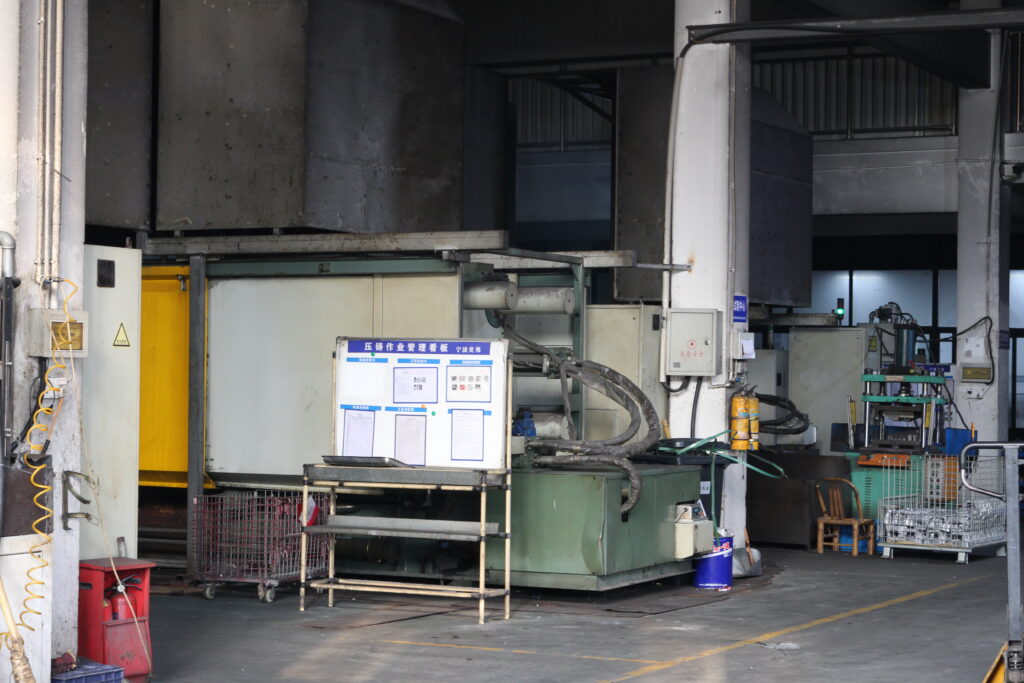
2.1. Die Casting Machines:
Die casting machines form the backbone of the process, responsible for injecting molten metal into molds under high pressure. They come in various sizes and configurations, from small, high-speed machines for intricate parts to large, high-pressure machines for sizable components.
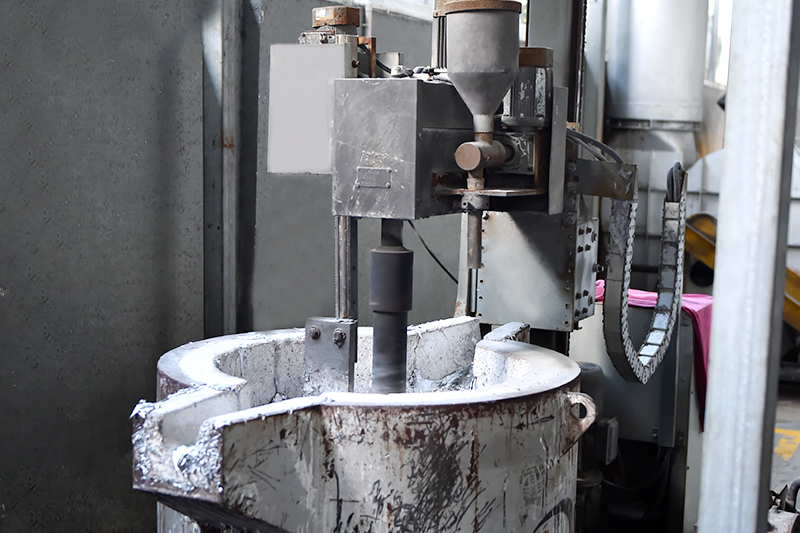

2.2. Molds:
Molds, also known as dies, are custom-made tools that shape molten metal into the desired form. Crafted from durable materials like steel or aluminum, molds endure high temperatures and pressures. Precision engineering ensures they withstand the rigors of the die casting process, crucial for determining final part shape and quality.
2.3. Furnaces:
Furnaces are essential for melting the metal alloys used in die casting. They’re designed to rapidly reach high temperatures and maintain precise control throughout the process. Furnace size and configuration vary depending on the operation’s scale and requirements.
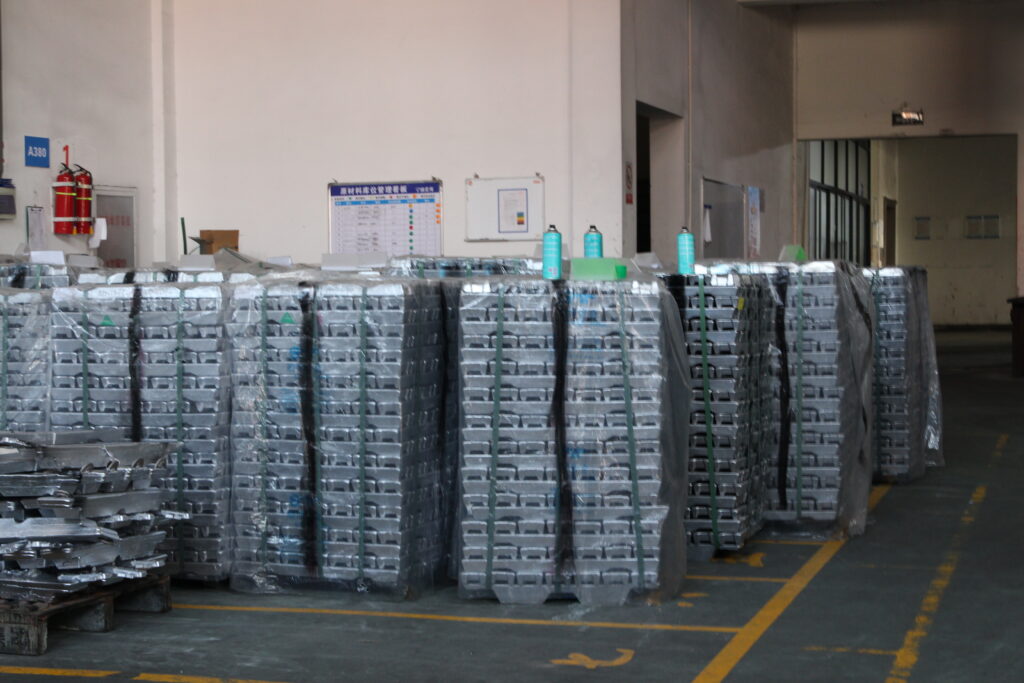
3. Delving into Die Casting Materials:
Materials are pivotal in determining product performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Let’s explore the characteristics and applications of commonly used die casting materials:
3.1. Aluminum Alloys:
Aluminum alloys are favored for their strength, lightweight properties, and corrosion resistance. Common alloys include:
– Aluminum 380 (A380)
– Aluminum 383 (A383)
– Aluminum 413 (A413)
These alloys offer versatility and can be tailored to meet specific performance needs, making them ideal across various industries.

3.2. Zinc Alloys:
Zinc alloys boast excellent casting properties, dimensional stability, and surface finish. Notable alloys include:
– Zamak 3
– Zamak 5
– ZA-8
They’re prized for their cost-effectiveness and ability to produce intricate parts with thin walls and complex geometries.
3.3. Magnesium Alloys:
Magnesium alloys offer the highest strength-to-weight ratio, making them ideal for weight-sensitive applications. Common alloys include:
– AZ91D
– AM60B
– AS41B
Favored for their lightweight properties and recyclability, magnesium alloys find use in industries focused on energy efficiency.
Die casting techniques vary based on how molten metal is introduced into the mold cavity. Let’s explore each classification:
4. Understanding Die Casting Techniques:
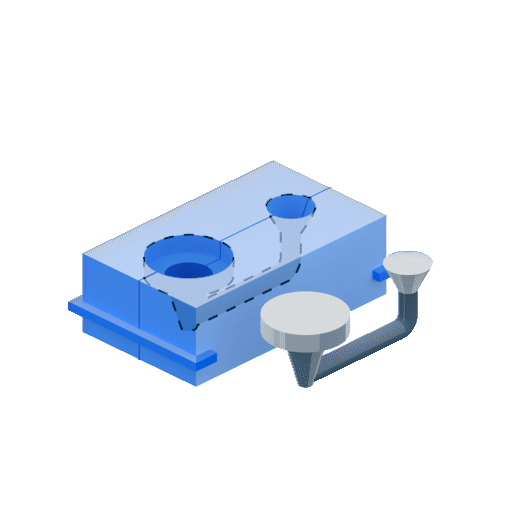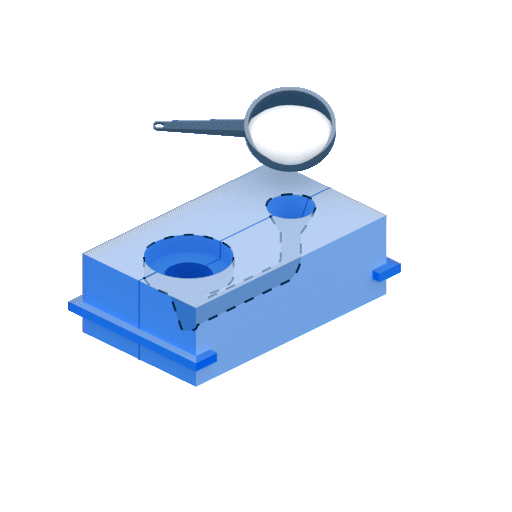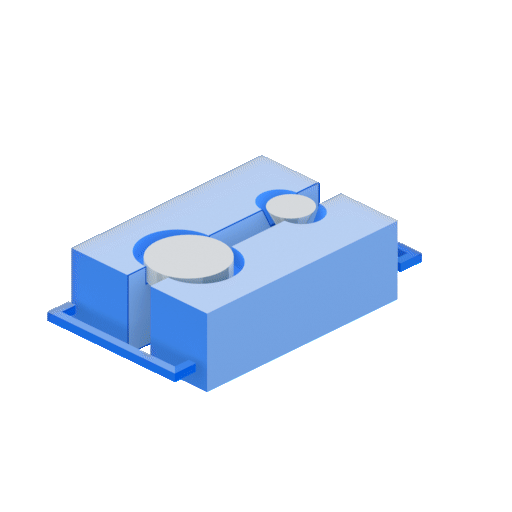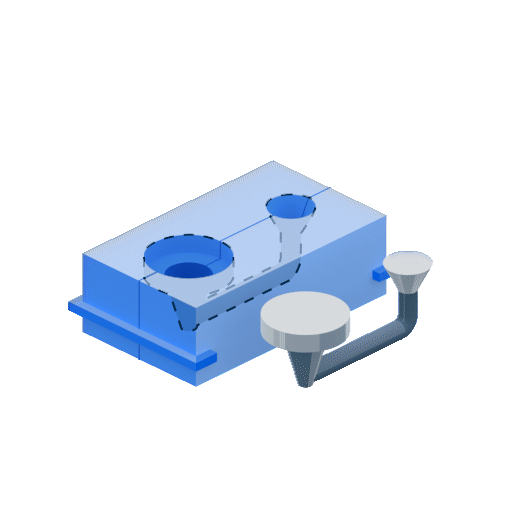
4.1. Gravity Die Casting:
Involves pouring molten metal into a mold using gravity, ideal for high-quality parts with excellent surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
4.2. Low Pressure Die Casting:
Utilizes pressurized furnaces to force molten metal into molds at low pressure, suitable for complex parts with thin walls and intricate geometries.
4.3. High Pressure Die Casting:
Injects molten metal into molds at high speed and pressure using hydraulic presses, ideal for high-volume production of parts with tight tolerances and complex shapes.
4.4. Vacuum Die Casting:
Uses vacuum chambers to remove air and gases from the mold cavity before pouring molten metal, eliminating porosity and improving casting quality, especially for intricate parts.
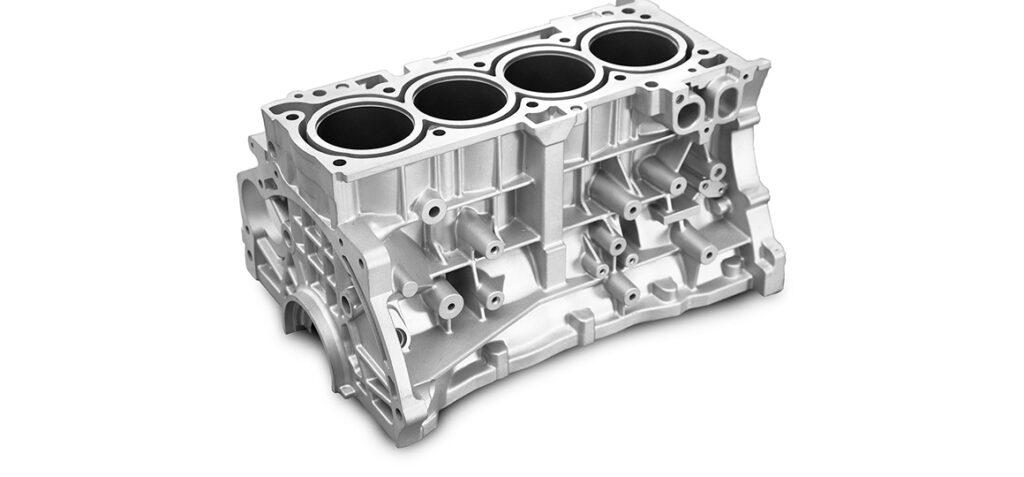
5. Applications of Die Casting:
Die casting finds applications across industries, from automotive and aerospace to electronics and consumer goods. It’s used to craft components like engine blocks, transmission cases, and suspension parts, ensuring precision and efficiency.

Conclusion:
Die casting continues to drive innovation in modern manufacturing, offering unmatched precision, efficiency, and versatility. Understanding its principles, equipment, materials, and techniques provides a deeper appreciation for its impact across various industries. As technology evolves, die casting remains at the forefront, shaping the products that define our daily lives. By embracing its intricacies, we unlock endless possibilities for innovation and progress in manufacturing.

